PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
APPLICATIONS
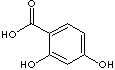
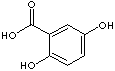
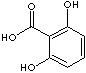
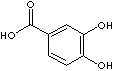
There are six isomeric compounds of dihydroxybenzoic acids which have two -OH groups and one carboxylic group on the benzene ring.
|
2,3-Dihydroxybenzoic acid |
2,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid |
2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid |
|
|
|
|
|
CAS
RN: 303-38-8 |
CAS
RN: 89-86-1 |
CAS
RN: 490-79-9 |
|
|
|
|
|
2,6-Dihydroxybenzoic acid |
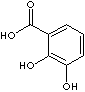
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid |
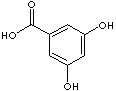
3,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid |
|
|
|
|
|
CAS
RN: 303-07-1 |
CAS
RN: 99-50-3 |
CAS
RN: 99-10-5 |
Gentisic acid, having a carboxylic group and two -OH at quinol position, is a crystalline powder that forms monoclinic prism in water solution. It is soluble in water, alcohol, ether, polar organic solvents and salts; sublimes at 200C and lemts at 205 C. 5-Hydroxysalicylic acid is another structural name of gentisic acid. Benzoic acid derivatives substituted by hydroxy group or ether containing oxygen atom have active bacteriostatic and fragrant properties. They are typically used in pharmaceutical and perfumery industry. The destructive metabolic property of oxygen containing benzoic acid derivatives such as protocatechuic acid (3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid) and veratric acid (3,4-dimethoxybenzoic acid) is used in the application for pharmaceuticals. Protocatechuic acid is a catabolite of epinephrine. Protocatechuic acid itself is used as an anticarcinogenic agent. Prazosin, a peripheral vasodilator and antihypertensive, is also an example of the applicaion of veratric acid. Hydroxyl group substituted benzoic acids feature analogue metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic Acid). Diacetate ester of 2,3-dihydroxybenzoic acid, dipyrocetyl, is an analogue of aspirin used as an analgesic and antipyretic. Dihydroxybenzoic acids are used as intermediates for pharmaceuticals (especially for antipyetic anlgesic, antirheumatism) and other organic synthesis. They are used as matrix for ionization of peptides, proteins and carbohydrates. In industrial field, they are used as intermediates for the production of other organic chemicals, resins, polyesters, plasticizers, dyestuffs, preservatives, and rubber chemicals.
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
99.0% m in
MELTING POINT
0.5% max
0.1% max